Toys related to Particle Accelerators
Most of the demonstrations shown below were produced with staffs of the SPring-8 Storage Ring for the SPring-8 OpenLab
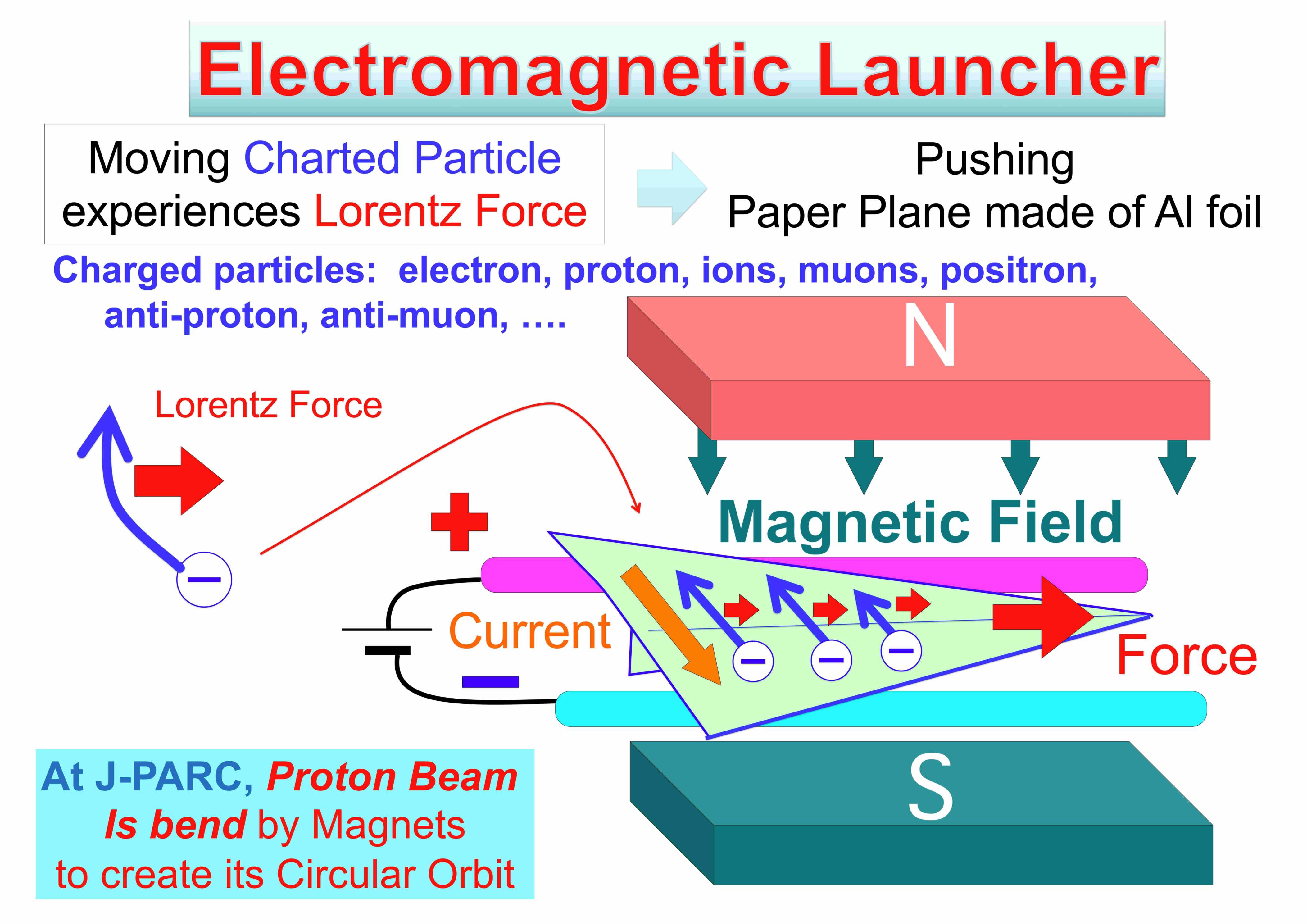
Acceleration by Lorentz Force
Lorentz Force Launcher ( Electromagnetic Launcher )
Origamied aluminum foil plane is placed between two rails that
are immenced in magnetic field.
the electric current flows in the plane
with perpendicular direction to the magnetic field and the launching direction,
and the Lorentz force on the current pushes and launch the plane
Lorentz Force Launcher
( Lorents force = one of electromagnetic forces )

Fleming's left-hand rule to show the relation of the directions
of electromagnetic force, magnetic field and electric current.
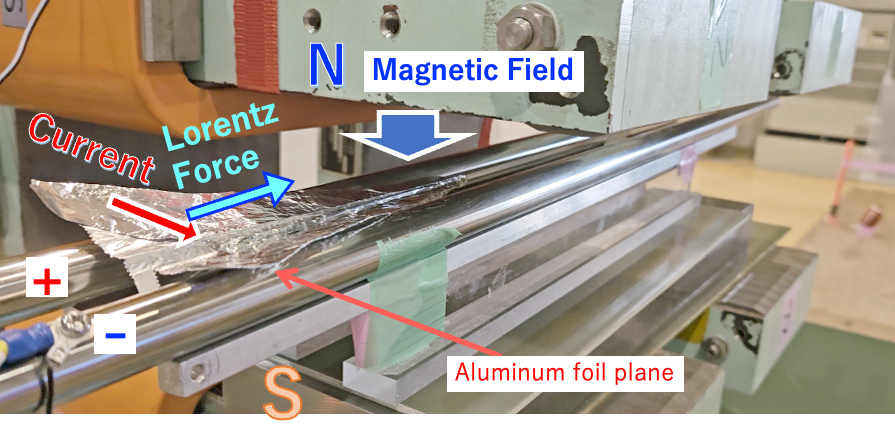
Test Flight at the SPring-8 Storage Ring OpenLab,
with the Storage Ring Beam Steering Magnets.
In this movie, the design of the plane is not good for the launcher (no straight flight stability ). The planes origamied by children hit the left wall (~10m flight distance).

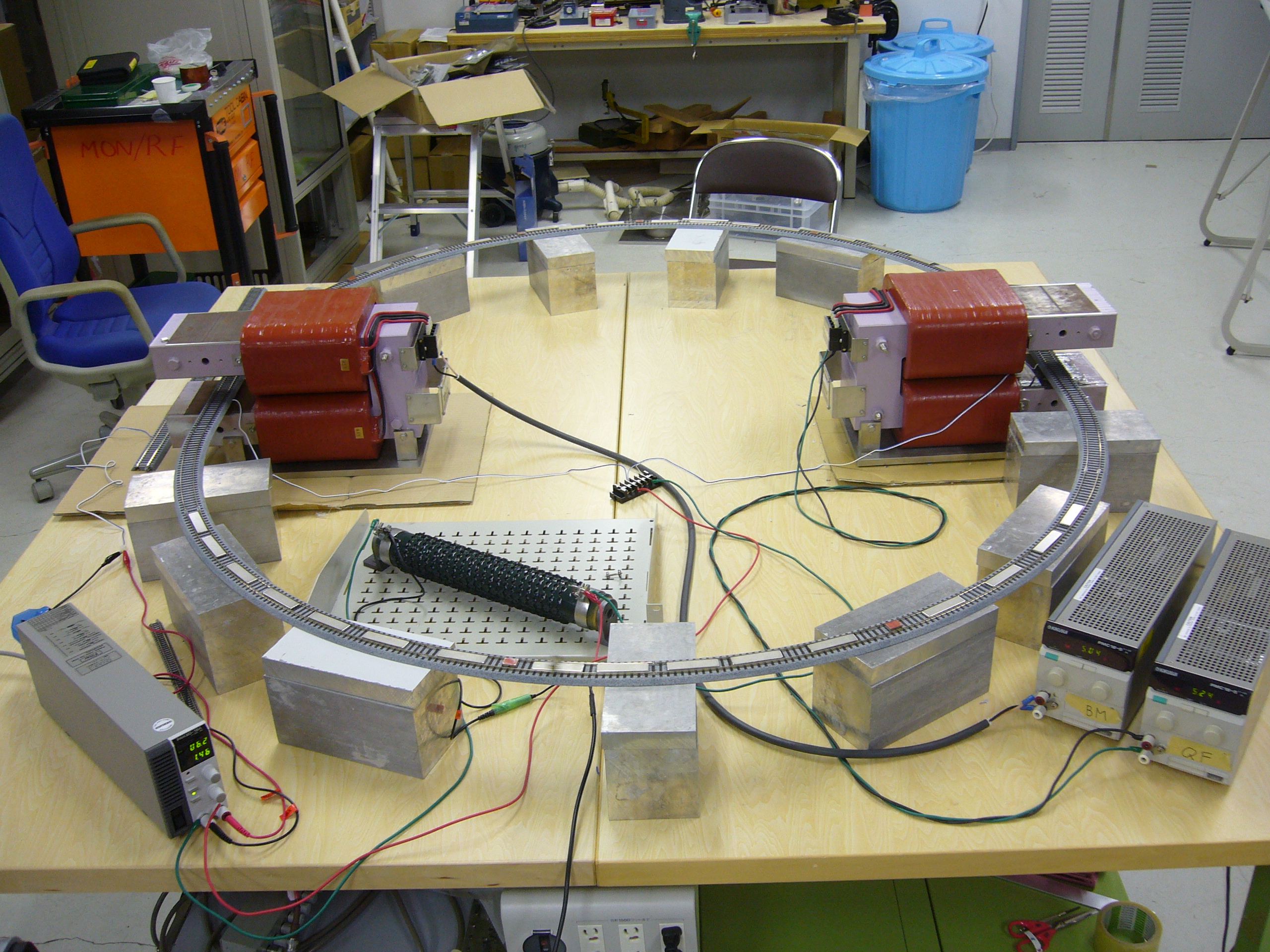
Test Flight at J-PARC (KEK)
with KEK B-Factory Beam Steering Magnets.
Demonstration at KEK J-PARC OpenLab 2023
-------- -------- --------
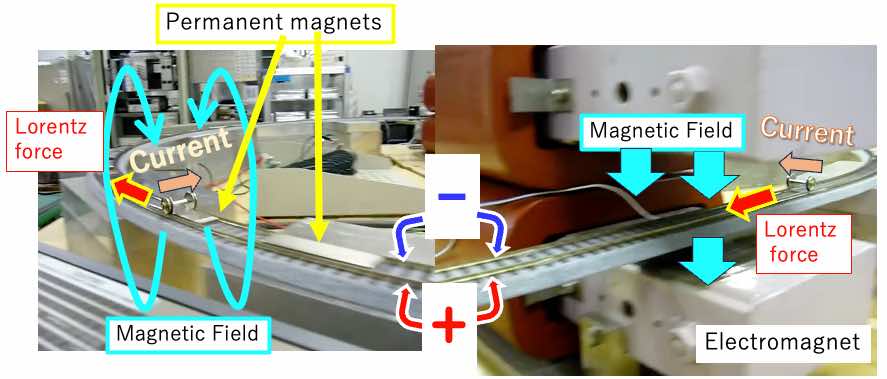
Wheels driven by Lorentz force
Demonstrated at SPring-8 OpenLab Strage Ring Section:

Charged particles such as electrons moving in a magnetic field will experience a force called the Lorentz force.
This force is perpendicular to both the direction of the particle's motion and the direction of the magnetic field. The magnitude of the force is given by the product of the charge of the particle, the magnitude of its velocity, and the strength of the magnetic field.
In the case of a conductor carrying a current by the moving electrons, the electrons experience the Lorentz force
due to the magnetic field. However, electrons are confined in the conductor,
the Lorentz force
This force results in the conductor experiencing a mechanical force, which is commonly known as the "magnetic force."
In this toy, a voltage between the two rails are applied to create a current flow along the axis of the wheels.
The vertical magnetic field created by the electromagnets and NdFeB permanent magnets will then cause the electrons in the conductor to experience the Lorentz force, resulting in a mechanical force on the conductor, which can cause the wheels to move.
This phenomenon is the principle behind electric motors,
where the interaction between a magnetic field and a current-carrying conductor generates mechanical motion.
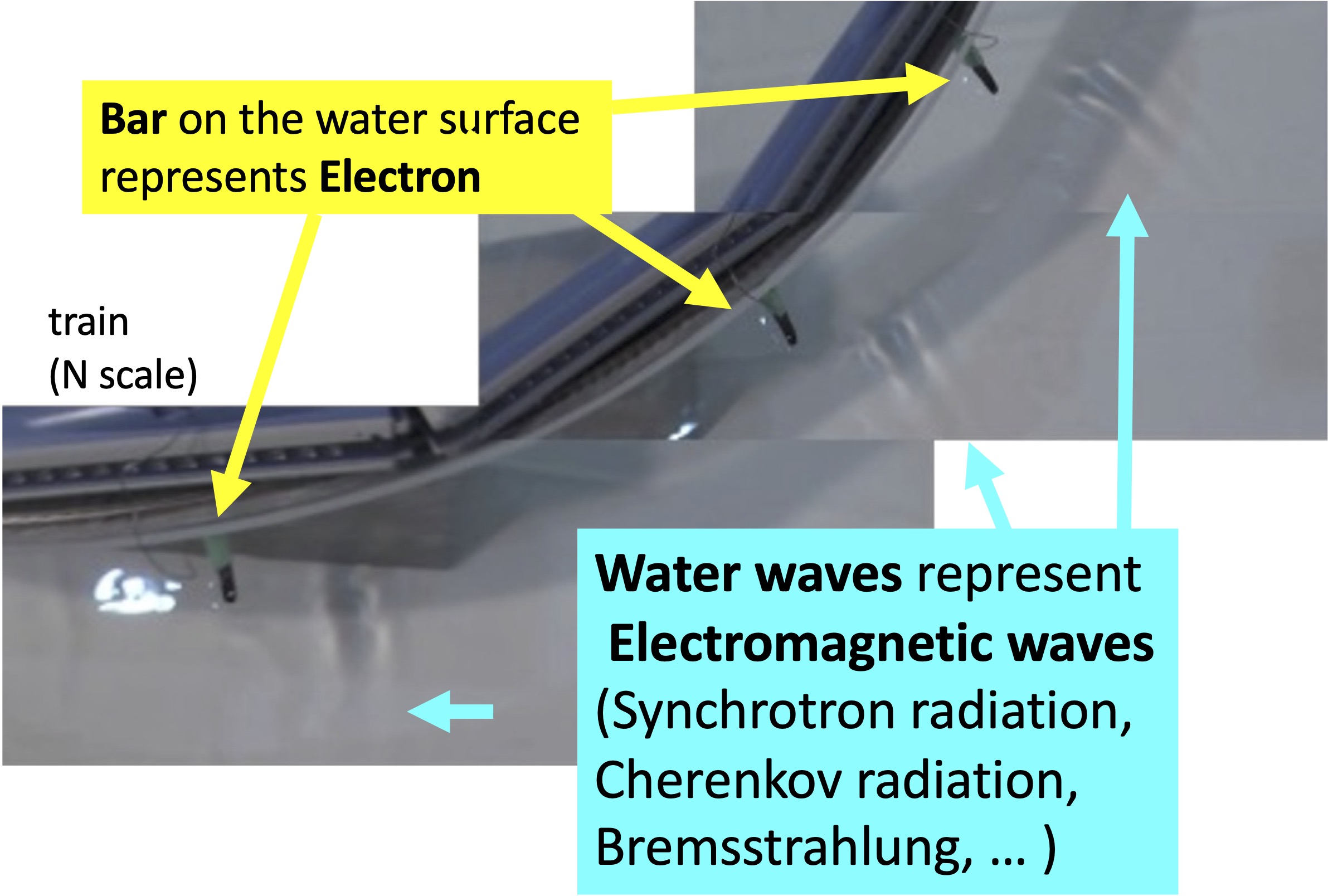
Synchrotron Radiation, Cerenkov Radiation and Bremsstrahlung:
Light generated by Fast Electron, simulated with water waves
Demonstrated at SPring-8 OpenLab Storage Ring Section:
Light: X-ray, radio wave, gamma ray, infra-red, ultra-violet,.. is a electromagnetic wave,
therefore, can be simulated with water waves in some cases.
Here, we simulated the generation of electromagnetic waves by an electron with water wave.
An electron is simulated with a bar down to the water
surface from a toy train. The waves produced by the bar
simulate the electromagnetic wave ("light") emitted from the electron.
The mechanims of generation of
synchrotron radiation, Cherenkov radiation and Bremsstrahlung are shown below.
In the floowing images and videos, the wave images are slightly advanced than the bar (wave source).
Its because the wave image is formed at the bottom surface of the water tank and
the lighting is not normal to the water surface.
Synchrotron Radiation
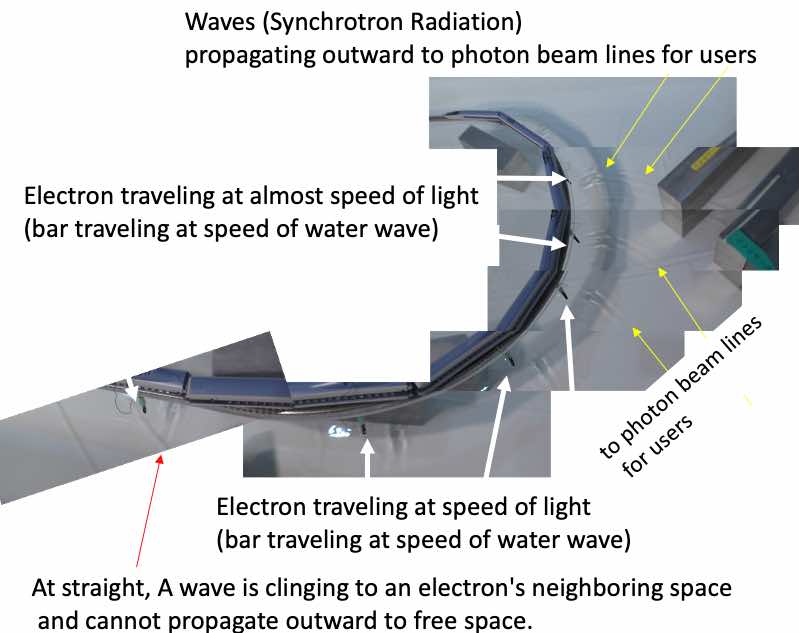
Electromagnetic waves are emitted when a high-speed electron that follows curved trajectories.
An electron always produces Electromagnetic field around it.
Electromagnetic field (EM field) around the electron has a non-zero distance from the electron,
so it takes time for the EM field to notice that the electron has changed its course and
the electromagnetic wave (EM wave) leaves the electron and travels straight,
with deccelationg the electron for the EM field to get the energy to become the EM wave.
And finally the EM field becomes EM wave pulse including "visible light",
"radio wave", "infra-red", "ultra-violet",
and, "x-ray" if the electron has enough speed almost the speed of light.
The closer the speed of electrons is to the speed of light,
the shorter electromagnetic wave is produced.
The EM field generated by an electron is compressed
by Lorentz contraction in the direction that the electron is travelling.
The thinner the EM field due to compression by the Lorentz contraction,
the shorter wavelength EM wave is produced by the electron.
In order to produce short wavelength radiation like X-ray,
of which wave length is less than 1/100,000,000 meters,
it is necessary
to bring their speed closer and closer to the speed of light,
by acceleratting an electron, or giving the kinetic energy oo it
comparable to the acceleration by 10,000,000,000 Volts.
Therefore, all synchrotron radiation rings are large devices to produce high energy electrons.
For the electron with straight motion,
in the electron's rest frame ( where the electron looks "stop"), the EM field is just the Coulomb isotropic static electric field, and no EM wave exists.
For the lab frame ( where the electron is moving ), the EM field is mixture of the electric field and magnetic field. However, the field cannot leave the electron and cannot make EM wave.
Cherenkov Radiation, Bremsstrahlung and Synchrotron Radiation in water wave

