Concept
We expand capability of time-resolved X-ray solution scattering for studying strucutral dynamics of photochemistry.
本研究課題では、パルスX線による光化学反応の構造ダイナミクス研究の可能性を飛躍的に拡大します。
In this project, we will increase the sampling frequency of the X-ray scattering signal by about three orders of magnitude, which will improve the S/N ratio by about 30 times. This makes it possible to directly observe the change of molecular structure in solution even for molecules consisting only of lighter elements in the first to third periods of the periodic table. This will dramatically expand the range of molecules to which this method can be applied, which will promote a new research field in ultrafast molecular structure science.
時間分解X線溶液散乱法は、溶液中の光化学反応に伴う分子構造の変化を「あたかも分子の動画を撮影するように」直接観察できるとてもユニークな実験手法です。しかしこれまでは、実現可能な測定のS/N比の限界があり、金(Au)やヨウ素(I)など、元素周期表の第5周期や第6周期より下に位置する重元素を含む試料しか測定対象にできないという大きな課題がありました。
本研究課題では、X線散乱信号のサンプリング周波数を約3桁上げることで、測定のS/N比を約30倍向上させます。これにより、周期表の第1周期から第3周期の軽い元素だけで構成される分子でも、溶液中の分子構造の変化を直接観察することが可能になるはずです。この改良により、本手法の測定対象となる分子の適用範囲を飛躍的に拡大することで、「超高速分子構造科学」を推進します。
Project
This project is mainly conducted at the PF-AR, KEK.
本研究課題は、高エネルギー加速器研究機構(KEK)の放射光蓄積リングPF-ARで主に実施します。
The construction of MHz repetition rate X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) facilities using superconducting cavity technology is currently underway around the world. The measurement method developed in this research project is expected to become a fundamental technique for measuring the dynamics of chemical reactions on the femtosecond order, which is expected to be one of the important application research fields at the MHz repetition rate XFEL facility in the hard X-ray region in about 5 to 10 years.
KEKのPF-ARは、1つの電子バンチだけが蓄積リングを周回する運転モード(シングルバンチモード)で運転されています。電子が蓄積リングを1周するのに必要な時間は1.26マイクロ秒で、これは794kHzの繰り返し率(放射光の周波数)に相当します。この繰り返し周波数(794kHz)をX線散乱測定のサンプリング周波数として用いることで、従来の測定(1kHz)に比べてサンプリング周波数が3桁向上し、測定のS/N比として30倍の向上が実現します。
現在、超伝導加速空洞技術を活用したMHz繰り返しのX線自由電子レーザー(XFEL)施設の建設が世界各地で進行しています。これらの施設においては、今後5〜10年以内に、硬X線領域でのMHz繰り返しフェムト秒X線の利用実験が次々と開始されると見込まれます。本研究課題で開発する実験手法は、MHz-XFELの重要な利用研究の一つとして想定されるフェムト秒オーダーの化学反応ダイナミクス計測のための基盤的な計測技術となります。
News
Current status of the project
研究課題の進捗状況
News #4
Edge Article / Chemical Science
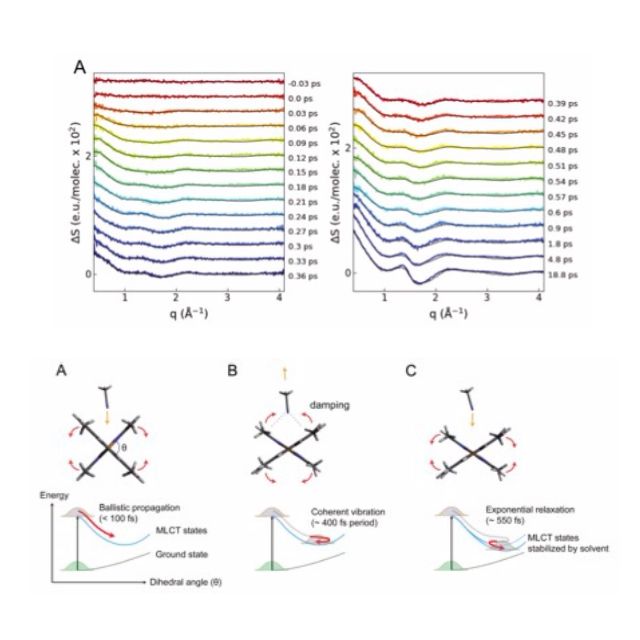
X線溶液散乱の共同研究論文
"Atomic-scale observation of solvent reorganization influencing photoinduced structural dynamics in a copper complex photosensitizer"
T. Katayama, T.-K. Choi, D. Khakhulin, A. O. Dohn, C. J. Milne, G. Vanko, Z. Nemeth, F. A. Lima, J. Szlachetko, T. Sato, S. Nozawa, S. Adachi, M. Yabashi, T. J. Penhold, W. Gawelda, G. Levi
Chem. Sci., 14, 2572-2584 (2023).
10.1039/D2SC06600A
News #5
J. Phys. Chem. Lett.
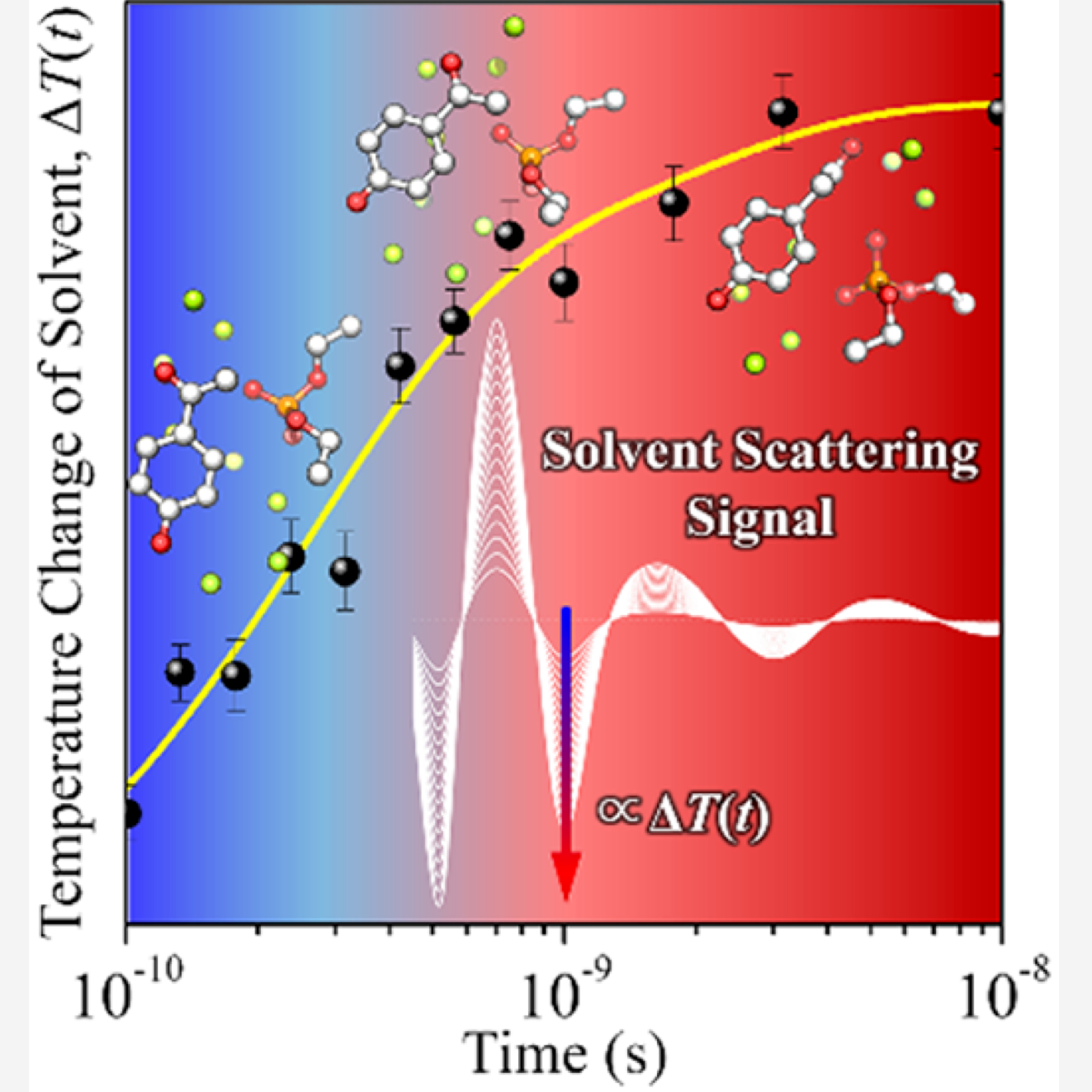
X線溶液散乱の共同研究論文
"Extracting kinetics and thermodynamics of molecules without heavy atoms via time-resolved solvent scattering signals"
K. Y. Oang, S. Park, J. Moon, E. Park, H. K. Lee, T. Sato, S. Nozawa, S. Adachi, J. Kim, J. Kim, J.-H. Sohn, H. Ihee, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 3103–3110 (2023).
10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c00041
News #6
no title

News #1
Grant Approval (May 18, 2021)

2021年5月18日に、科研費交付の内示をいただきました。
News #2
Edge Article / Chemical Science
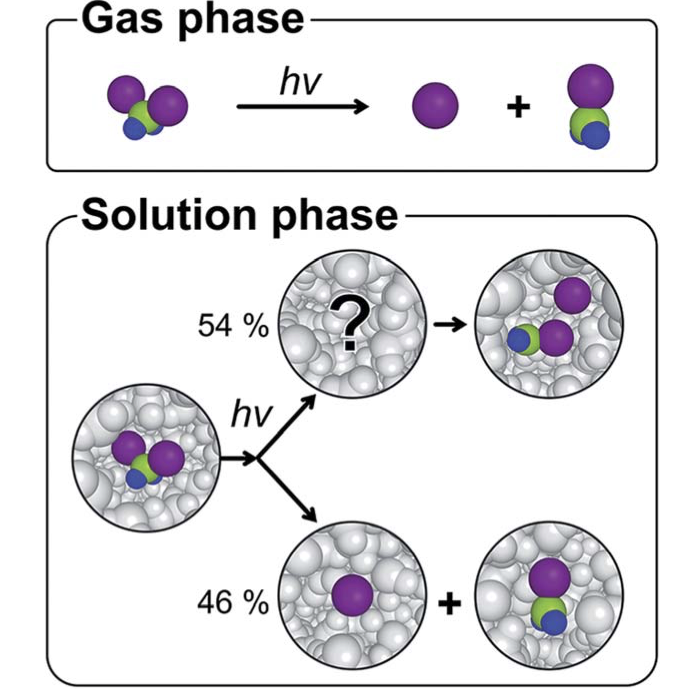
共同研究論文
"Ultrafast structural dynamics of in-cage isomerization of diiodomethane in solution"
Hanui Kim, Jong Goo Kim, Tae Wu Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Shunsuke Nozawa, Shin-ichi Adachi, Kihwan Yoon, Joonghan Kim and Hyotcherl Ihee
Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 2114
(DOI: 10.1039/d0sc05108j)
News #3
Accounts of Chemical Research
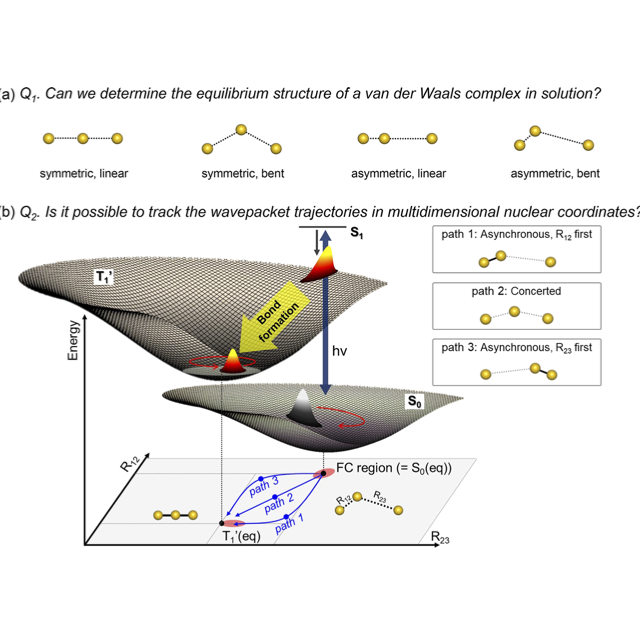
共同研究グループによるレビュー論文
"Femtosecond X‐ray Liquidography Visualizes Wavepacket Trajectories in Multidimensional Nuclear Coordinates for a Bimolecular Reaction"
Jong Goo Kim, Eun Hyuk Choi, Yunbeom Lee, and Hyotcherl Ihee
Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 1685−1698.
(doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00812)
元論文は、こちら "Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation"
Kim et al., Nature 2020, 582, 520−524.
(10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3)
About Us
Group Members
| Principal Investigator (PI) | Shin-ichi Adachi (KEK) |
|---|---|
| Co-PI | Shunsuke Nozawa (KEK, IMSS) |
| Co-PI | Testuo Katayama (JASRI, SACLA) |
| Researcher | Ryo Fukaya (KEK, IMSS) |
Contact
Shin-ichi Adachi
Executive Director,
High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK)
1-1, Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801, Japan
e-mail: shinichi.adachi(at)kek.jp
HP: http://research.kek.jp/people/adachis/